Plastic Blowing machine
Introduction
A plastic blowing machine is a specialized piece of equipment used to manufacture a wide range of plastic products. It works by heating a molten plastic material and then forcing it through a die to create the desired shape. The blowing machine is capable of producing items such as bottles, containers, beverage holders, and other hollow objects. It is an essential tool for any plastics production facility, as it allows for efficient and cost-effective fabrication of products.
The plastic blowing machine works by using a combination of heat and pressure to mold the molten plastic material. The raw material is fed into the machine’s hopper and heated to its melting point in an oven or furnace. The molten material is then forced through a die that has been created with the specific shape desired for the product. During this process, pressurized air is blown through the material to push it outward into the die and shape it accordingly.
The plastic blowing machine offers several advantages to companies that use it for production. It allows for fast production times as well as increased accuracy and repeatability when creating complex shapes and forms. Additionally, since the machine uses air pressure rather than mechanical force to form the plastic, it eliminates many potential safety hazards associated with traditional manufacturing processes.

A Plastic Blowing Machine is a highly efficient and reliable piece of machinery used to produce plastic products. It uses air pressure to blow heated plastic into a mold, creating a finished product with consistent quality and a smooth finish. It is suitable for producing small and large items, from bottles to toys. The Plastic Blowing Machine is easy to operate and maintain, making it an ideal choice for businesses of all sizes. Its flexibility allows manufacturers to create a wide variety of products, while its efficiency ensures that production costs are kept low. Thanks to its durability and low maintenance costs, the Plastic Blowing Machine is an invaluable tool in the plastics industry.
Plastic blowing machines are widely used in the production of a variety of plastic products. These machines use air to inflate molten plastic into a shape that is determined by a mold. By using these machines, manufacturers are able to create complex and intricate shapes quickly and cost-effectively. The process of plastic blowing requires specialized knowledge and expertise to ensure that the finished product meets the desired specifications.
Plastic blowing machines typically consist of an extruder, a hopper, a die, and a cooling system. The extruder melts the plastic pellets in the hopper and forces them through the die. As the plastic exits through the die, air is injected to inflate it into the desired shape. Once it has been inflated, it is cooled with air or water before being removed from the mold.
The plastic blowing process can be used to produce items from small toys to large automotive components. It is also used in medical equipment manufacturing due to its ability to create complex shapes quickly and efficiently. With advancements in technology, plastic blowing machines are becoming more efficient and capable of producing higher quality products at faster speeds.
By using plastic blowing machines, manufacturers can reduce costs while still creating high-quality products that meet their needs.
Blowing process
Blow molding is a fairly straightforward process that involves melting, homogenizing, extruding, (blow) molding, cooling, and ejecting. Different manufacturing plants may use additional processes such as additional heating or cooling cycles, additives, and compound colourants. These additional processes depend on the design and intended application of the final product.
Feeding the plastic with resin or charging: The first step in the blow molding process is feeding the plastic. This is done by transferring plastic pellets to the extruder hopper. Vacuum pumps siphon pellets from big bags or bulk containers and transport them to raw material silos or hoppers. The rotary feeder at the bottom of the silo controls the feeding rate of the paste or extruder. Compressed air is then used to transfer the stored pellets to the extruder hopper. In other systems, plastic pellets from bags or big boxes can be vacuum conveyed directly into the hopper of the extruder without the need for a separate air conveyance system.

Plasticizing or Melting
Continuous kneading and heating melt the plastic resin as it enters and passes through the extrusion process. To melt the polymer, electric heating elements or heating bands are wrapped around the extruder barrel. The extruder screw is divided into pieces, each of which serves a distinct purpose. There are three of them: feeding, compressing, and metering. The extruder screw is intended to generate enough shear and compression to homogenize and extrude the plastic.

Then the plastic is transferred from the screw to the accumulator head and the temperature of the plastic is stabilized through the heaters installed on the head to prepare it for blowing and distributing the raw material by the parison.
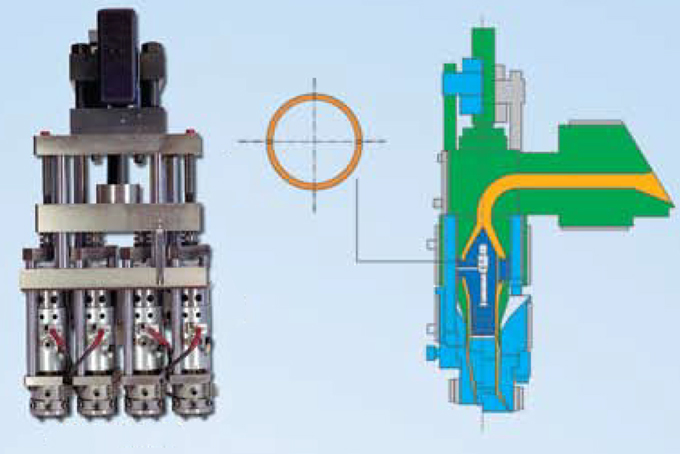

Parison Extrusion
Parison control means dynamically controlling the thickness of the Parison to obtain a uniform thickness container on an extrusion blow molding machine. Helps maintain required thickness axially and radially on product made with extrusion/injection blow molding (BM).
What exactly is Parison?
It is the tubular shape of molten plastic produced by extruding or injecting on a Blow Molding machine. This viscous melt plastic known as Parison is placed in two halves of Blow Molds and molded to the shape of the cavity of the mold by blowing compressed air.

Why is control necessary?
The Parison will be molten as it comes out of the BM machine’s die head. The Parison will stretch as a result of the self-weight, resulting in a thinner top part relative to the bottom portion. This will result in an inconsistent thickness in the finished piece. In order to get a more consistent product wall thickness, the various geometries of the product to be moulded need altering the parison thickness.
The advantage of Parison
- Uniform article wall thickness and hence enhanced quality as a result of lower thermal stresses during processing.
- Weight reduction is possible due to the balanced distribution of thickness.
- Reduced top and bottom wastage, resulting in increased output.
- Reduced cooling time owing to thickness homogeneity, resulting in increased output.
Control in a closed loop (Multi-point Parison Programmer)
To adjust the parison thickness at various places, a closed loop electro-hydraulic control system can be installed on the machine (30 times or 100 times or more). Because this is a closed loop system, the precision is significantly higher than in a typical system, and the finished container has the most uniform thickness.
Control of Axial Wall Thickness
All of the technologies discussed above are for controlling thickness in the axial direction of Parison. This is one of the most often used Parison controllers.
Control of Radial Wall Thickness (PWDS)
Aside from axial wall thickness control, some particular and complicated products require radial wall thickness control. This is accomplished by converting the uniform circular space through which parison emerges to an elliptical shape.
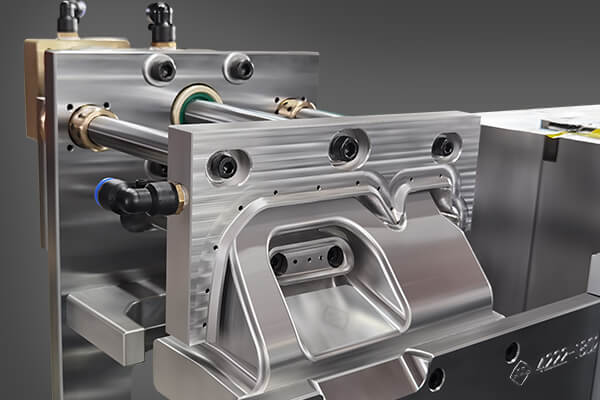
Clamping or sealing:


It contains two copper poles and an electric heater. It is connected to a low-voltage and high-current transformer to generate sufficient heat to cut the plastic tube.
Inflation or blow molding:

Cooling and Ejecting:
The cooling process comes next. Typically, as the plastic touches the die, it cools at a predetermined rate, stabilizing the product’s dimensions. After cooling by using chiller with cold temperature around10 C to 17 C, the mold opens and the product is ejected.
Trimming ( deflashing system):
Flashing is common in extrusion blow molding. As the dies clamp the preform, most blow molding machines have auto deflashing features. However, flash can be found at the top and bottom of the product, particularly at the opening where compressed air is injected. A rotating knife is used to trim the excess material. Some systems collect excess materials, grind them, and feed them back into the extrusion machine to reduce waste.

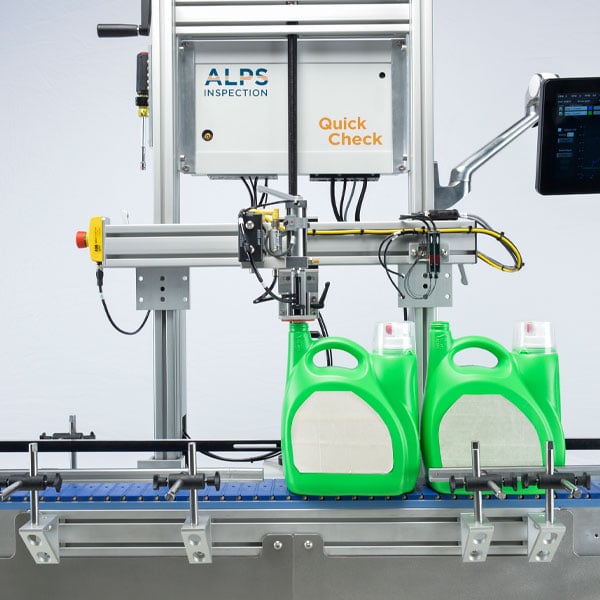
Leak test system:
This is the standard quality control method used in the production of bottles or packaging materials. Inside the container, either vacuum or compression is generated in this step. The machine will then monitor the pressure to see if air enters or escapes the container. If a leak from the container is detected, it is rejected and fed back into the system.


