Guide to DC Servo Motors
DC servo motors are integral components in a wide range of applications requiring precise control of position, velocity, and torque. This guide explores the fundamentals of DC servo motors, their working principles, types, applications, advantages, and maintenance tips.
Understanding DC Servo Motors
DC servo motors utilize direct current (DC) to facilitate precise control over speed and position. Let’s delve into the core components and workings:
Key Components
- Stator: Contains the stationary windings that create a magnetic field.
- Rotor: Houses the rotating armature connected to the shaft.
- Commutator: Facilitates current flow to the rotor windings.
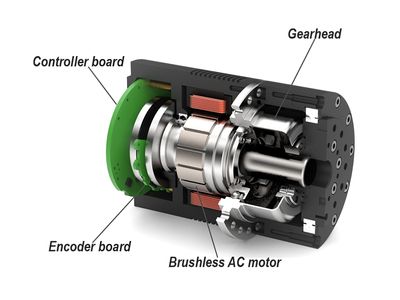
Working Principle of DC Servo Motors
DC servo motors operate on the same basic principles as other DC motors. However, they incorporate additional components to enable precise control. The main components of a DC servo motor system include:
- Motor: The DC motor generates the necessary rotational motion.
- Position Sensor: Often an encoder or potentiometer, it provides feedback on the motor’s position.
- Controller: It processes the feedback signal and adjusts the motor’s input to achieve the desired position or speed.
- Drive: It amplifies the controller’s signal to provide the appropriate current and voltage to the motor.
In a typical operation, the controller compares the desired position (setpoint) with the actual position provided by the position sensor. Any deviation results in an error signal, which the controller uses to adjust the motor’s input, correcting the error and achieving the desired position.
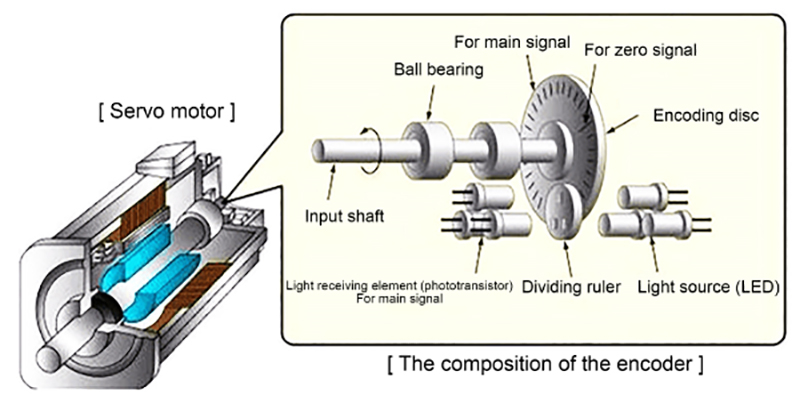
Types of DC Servo Motors
1. Brushed DC Servo Motors
Construction: These motors have brushes and a commutator that switch the current direction to keep the motor running.
Advantages: Simple design, cost-effective, and easy to control. Disadvantages: Brushes wear out over time, leading to maintenance requirements and potential for sparks.

2. Brushless DC Servo Motors
Construction: These motors do not have brushes. Instead, they use electronic commutation to switch current direction.
Advantages: Higher efficiency, longer lifespan, and low maintenance. Disadvantages: More complex and expensive than brushed motors.

Unraveling Efficiency and Performance
DC servo motors boast several advantages that render them indispensable in motion control systems. Here’s why they stand out:
Advantages of DC Servo Motors
- Precision Control: Seamlessly regulate speed and position with exceptional accuracy.
- High Torque: Deliver substantial torque for a wide range of applications.
- Efficient Operation: Optimize energy consumption for sustainable performance.
- Compact Design: Space-efficient solutions ideal for various installations.
- Reliability: Rugged construction ensures dependable performance in demanding environments.
Exploring Applications Across Industries
DC servo motors find application across diverse sectors, revolutionizing processes with their unmatched performance. Here’s where they excel:
- Industrial Automation: Drive conveyor belts, robotic arms, and assembly lines with precision.
- Robotics: Power robotic manipulators, grippers, and mobile platforms for versatile applications.
- Automotive: Control throttle valves, actuators, and position sensors in vehicles.
- Consumer Electronics: Enable precise movement in cameras, printers, and disk drives.
- Medical Devices: Facilitate accurate positioning in surgical robots, pumps, and diagnostic equipment.
Selecting the Perfect DC Servo Motor
Choosing the right DC servo motor entails a meticulous evaluation of various factors to match specific application requirements. Here are the key considerations:
1. Performance Requirements
- Torque: Determine the required torque for optimal performance.
- Speed: Define the desired speed range and response time.
2. Size and Form Factor
- Physical Dimensions: Ensure compatibility with space constraints and mounting requirements.
- Weight: Optimize weight for balance and portability.
3. Control and Feedback
- Feedback Mechanism: Choose between encoder, resolver, or potentiometer for precise position feedback.
- Controller Compatibility: Ensure seamless integration with your control system.
4. Environmental Considerations
- Operating Conditions: Ensure suitability for temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors.
- Protection: Consider IP ratings for protection against dust, moisture, and contaminants.
Maintenance
Proper maintenance of DC servo motors ensures longevity and reliable performance. Here are some maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspection: Periodically check for wear and tear, especially in brushed motors where brushes and commutators can degrade.
- Lubrication: Ensure that the bearings are well-lubricated to reduce friction and wear.
- Cleanliness: Keep the motor clean and free from dust and debris, which can affect performance.
- Check Connections: Regularly inspect electrical connections for signs of corrosion or looseness.
- Monitor Temperature: Ensure the motor does not overheat, which can be a sign of overloading or inadequate ventilation.
Conclusion
DC servo motors play a critical role in applications requiring precise control of motion. Understanding the types, working principles, and maintenance requirements of DC servo motors is essential for selecting the right motor for your needs and ensuring it operates efficiently over its lifespan. Whether you’re involved in robotics, manufacturing, aerospace, or automotive industries, DC servo motors offer the precision and reliability needed to achieve high-performance outcomes.
By following proper installation, configuration, and maintenance procedures, you can maximize the efficiency and longevity of your DC servo motor systems, ensuring they continue to deliver precise and reliable control for your applications.
FAQs
- What is the difference between brushed and brushless DC servo motors?
- Brushed motors use brushes and a commutator for commutation, while brushless motors use electronic commutation, resulting in different performance characteristics and maintenance requirements.
- Can DC servo motors be used in high-speed applications?
- Yes, but the choice between brushed and brushless may affect performance and maintenance needs at high speeds.
- How do I choose the right servo motor for my application?
- Consider factors like required torque, speed, precision, operational environment, and budget to select the most suitable motor.


It’s rare to come across texts that educate, inspire, and enchant all at once! Your article is not just a collection of information – it’s a true feast for the mind. Your words wrap around the reader like a warm blanket on a chilly evening, making them want to return again and again.
Hi there, I desire to subscribe for this blog to obtain hottest updates, so
where can i do it please help.